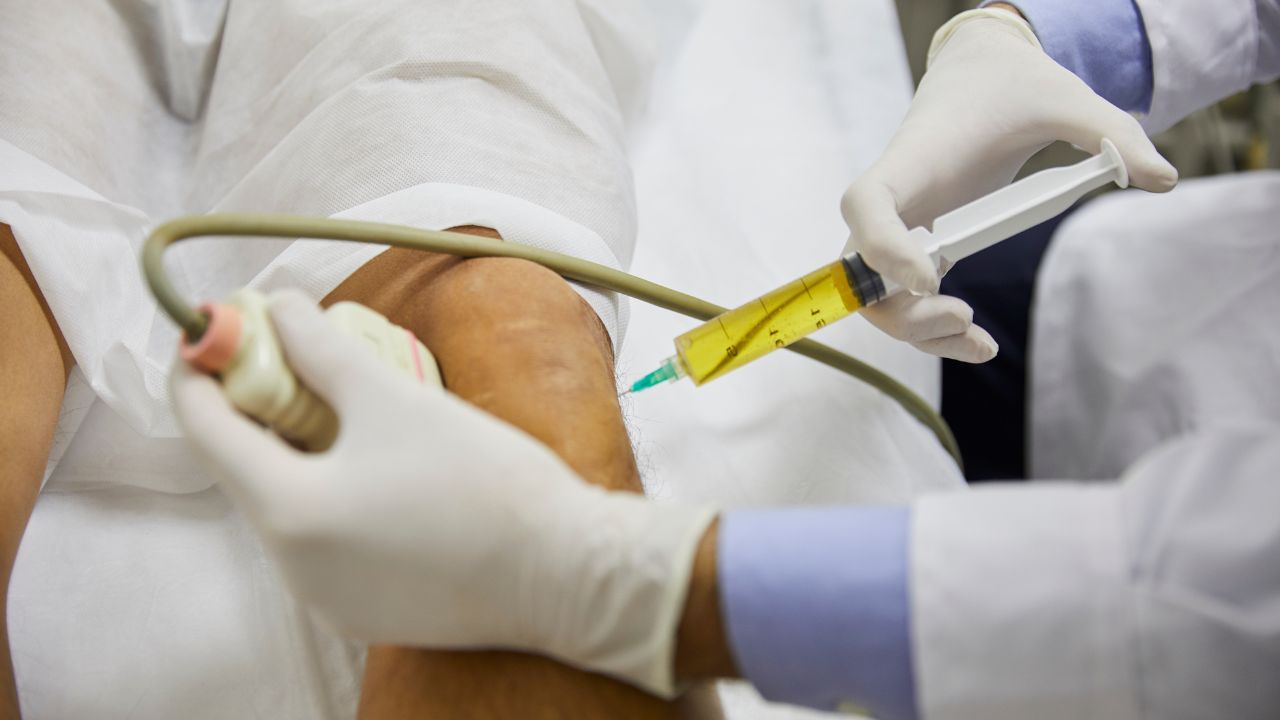
Stem cell treatments and PRP therapies aim to regenerate and alleviate pain caused by sporting activities and recreational exercisers, as well as seniors who are afflicted with wear-and-tear injuries or degenerative arthritis. Through stem cell therapy, individuals seeking relief from painful conditions can receive effective treatment at an expedited pace without the need for invasive procedures.
Contact us today to schedule your consultation with one of our healthcare providers to learn more about the treatments offered and available to you.
What are stem cells?
According to the National Institute of Health (NIH), stem cells are special cells that can differentiate into the various tissues in our bodies, such as muscle tissue, nerves, skin, and blood. They also have a crucial role during fetal development by acting as the fundamental cell types for all body systems – from the formation of tissues like fleshy and bone-like masses to replenishing dying organs until they eventually yield fresh ones again.
There are several types of stem cells, including adult stem cells, which can be found in the body and can continue to divide; embryonic stem cells, which are found in the early stages of development and can only divide a limited number of times; and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), which are created from mature skin cells that have been turned into pluripotent stem cells.
Types of stem cells
Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs)
Mesenchymal stem cells are adult stem cells extracted from a range of sources, such as bone marrow, adipose tissue (fat), umbilical cord tissue, and even amniotic fluid surrounding a fetus. Differentiation potential is exhibited by these adult progenitor cells that can be used therapeutically for regenerative purposes.
MSCs are found in every person’s bone marrow and accumulate during youth for eventual use to support the body’s healing process. As we age, however, their number and efficacy dwindle – a phenomenon commonly observed among all human life spans.
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), or stromal stem cells, can differentiate into a plethora of cellular fusions within the body; these include:
- Skin cells
- Bone cells
- Cartilage
- Muscle cells
- Neural cells
- Corneal cells
Autogenous MSCs & Autologous MSCs
Autogenous MSCs are typically derived from a patient’s own bone marrow or fat. Current scientific evidence supports the greatest benefit of stem cells extracted from bone marrow aspirate concentrate (BMAC), making it doctors’ preferred option for treatment and regeneration. On the other hand, additional stem cell research into functionalities, regenerative capacities as well as alleviating pain associated with those sources of MSCs is currently underway.
MSCs have been shown to promote regeneration and wound healing, as well as combat inflammation. In fact, MSCs have been found to improve outcomes in a wide variety of chronic diseases, including osteoarthritis, multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and spinal cord injury.
Allogeneic MSCs
Allogenic MSCs, or allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells, are a type of stem cell therapy that is gaining traction in the medical world. This type of stem cell therapy is unique because it uses stem cells taken from a donor and transplanted into the patient, allowing the patient to reap the benefits of the donor’s healthy cells. By doing this, researchers are able to use fewer stem cells than traditional therapies and still achieve great results. Allogenic MSCs have been shown to help with a variety of ailments and diseases, making them a promising treatment option for many.
Umbilical Cord Blood
Umbilical cord blood is a rich source of stem cells, which can be used for a variety of medical therapies. These stem cells have the ability to differentiate into various types of cells, including blood cells and immune cells. This property makes them useful for treating a wide range of diseases, such as blood cancers like leukemia and lymphoma, inherited immune system and metabolic disorders, and inherited blood disorders such as sickle cell anemia and thalassemia.
Umbilical cord blood stem cells are also being studied and used for their potential use in regenerative medicine. The procedure is relatively non-invasive, and it is easy to collect and process cord blood.
Cord blood banking is the process of collecting and storing umbilical cord blood for future medical use. Cord blood can be collected and stored at a cord blood bank, either privately or through the public cord blood donation program, in case the baby or family member may need it in the future.
What do stem cell injections do?
Stem cell therapy is a promising medical treatment that uses the self-renewal, immunomodulatory, and anti-inflammatory properties of stem cells to alter the physiology within the human body positively.
The stem cells used in the injections can either be taken from the patient’s own body or from a donor. The stem cells are then injected directly into the affected area, which repair and regenerate damaged tissue.
Injecting stem cells can help reduce inflammation, improve mobility, and even reduce pain. While stem cell therapy is still considered very new, it is showing promising results for many patients. If you are interested in exploring this option further, be sure to speak with your healthcare provider.
What can be the benefits of stem cell injections?
1. Cardiovascular Disease Treatment
According to clinical research being currently performed, stem cell therapy is an emerging and promising treatment for cardiovascular diseases. It involves injecting fresh stem cells into the affected area to improve cardiovascular function and regenerate healthy tissue. This therapy has been utilized to treat various conditions, including heart attacks and strokes, and shows great potential in cardiac regeneration and repair.
Since the first transplant into human patients, different types of stem cells, such as bone marrow-derived stem cells and embryonic stem cells, have been used in this field. The goal of stem cell therapy is to transplant enough cells into the myocardium at the site of injury or infarction to maximize the restoration of function.
2. Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases
Stem cell therapy is a promising new treatment for neurodegenerative diseases such as Huntington’s and Parkinson’s diseases. To slow or reverse the progression of the disease, a stem may be used to replace damaged cells. Recent clinical trials have been encouraging, providing evidence that stems cell therapy could be a viable option for treating these devastating illnesses.
3. Wound Healing
Research suggests that it can also help heal incisions and wounds. Stem cell therapy is gaining traction in the medical community as an effective way to help speed up the healing process of a patient post-surgery or other injuries. With the ability to jump-start the healing process, stem cell therapy offers patients a new option for faster recovery.
4. Orthopedic Conditions
Studies also show the potential for stem cells to help heal and regenerate damaged tissue. These treatments are becoming more available to patients with osteoarthritis, tendonitis, and ligament injuries. While there is still much to learn about the full capabilities of stem cell therapy, growing evidence suggests that it can be an effective treatment for many orthopedic issues.
5. Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune diseases occur when the body’s own immune system attacks healthy tissue. This can cause conditions like lupus, multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and Crohn’s disease. Stem cell therapy may reduce inflammation and stop the immune system from attacking its own cells.
STEM CELL AND REGENERATIVE TREATMENTS
Stem cell injections can be administered in conjunction with one’s surgical treatment, augmenting its effects or utilized as a solitary therapy for alleviating pain related to orthopedic conditions. Many patients who seek relief from excruciating joint issues opt to try this form of regenerative medicine in order to forego surgery altogether; success may often be attained through concomitant utilization of stem cells along with the procedure itself. By reducing infection risk and ameliorating postoperative inflammation, restoration time is shortened while also enhancing faster healing times and ultimately hastening return-to-normality after surgeries – all without any additional expenditure!
Stem cell injections can be augmented by conjoining them with other orthobiologic modalities like prolotherapy or PRP injection of the dextrose-saline solution. Platelets are believed to be home to myriad growth factors and cytokines which may aid in tissue regeneration; consequently, incorporating stem cells into the mix might generate an even more intense healing response.